TellusR Search
TellusR combines semantic search with traditional keyword-based search to deliver highly relevant results. While keyword search works immediately after installation, semantic search requires additional setup, as described below.
Setting Up Semantic Search
To enable semantic search, you must first generate semantic indexes.
A semantic index is a searchable index created by converting your documents into vector representations, known as embeddings. These embeddings capture the meaning and context of the content, allowing for more intuitive and context-aware search results.
Once a semantic index is set up, any new documents sent to TellusR via the API will automatically be added—provided they contain the necessary fields for indexing.
The default behavior is that queries performed with the /tellusr/api/v1/{project}/query GET and POST operations target all semantic indexes and their results are merged.
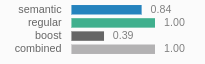
When checking out queries in the dashboard, the normalized semantic scores are displayed like this in the search result list:
You can manage your semantic indexes under Admin -> Indexing. Here you can configure new semantic indexes and see an overview of ongoing and completed reindexing tasks.
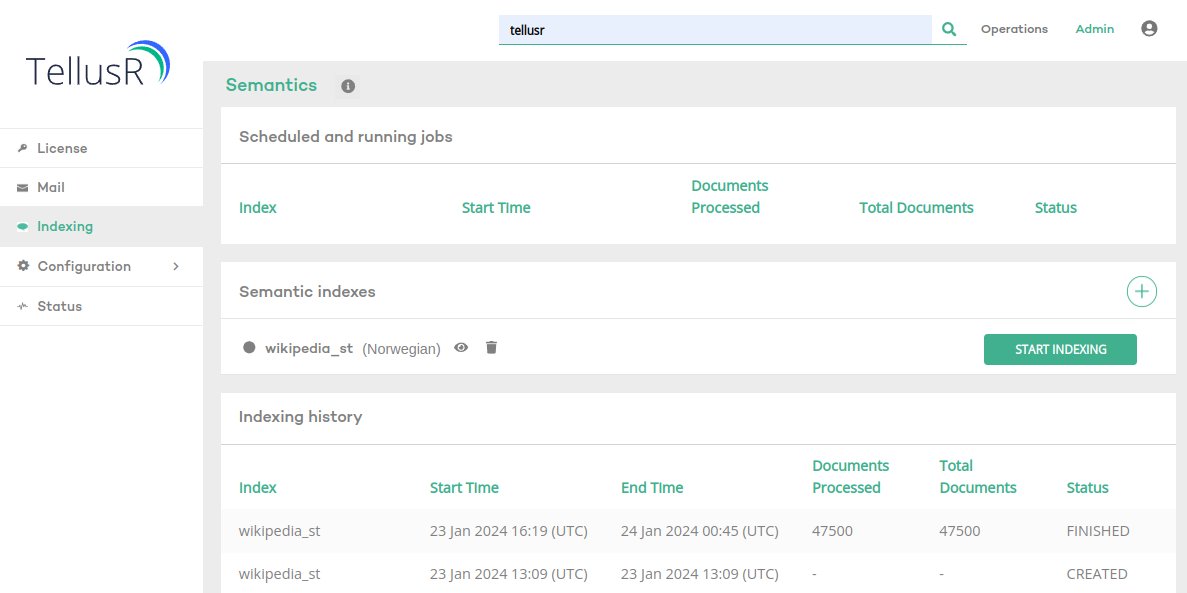
Pressing START INDEXING will reindex all documents from scratch. The search is available during indexing, but pressing START INDEXING will immediately replace the existing index.
Configure new semantic indexes
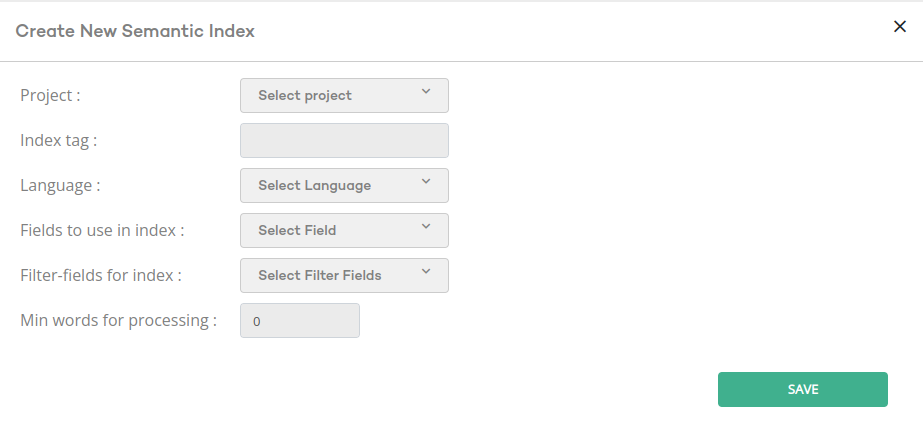
- Project: the project from which to take documents.
- Index tag: preferably a short descriptive tag of the index you are about to create. You will need this tag if you will configure search components manually. See Advanced Configuration.
- Language: Select a language. It is recommended to select a language that fits the language of your documents.
- Fields to use in index: Here you can specify which fields should be treated as the documents content. Their content is then joined and converted to an embedding.
E.g. if your documents have
titleandcontent_segmentyou can select both fields to create embeddings based on joining title with description. - Filter fields for index: Select fields to be indexed for each embedding in addition to the embedding. E.g. let’s say your documents have
categoryand you want to perform semantic searches filtered by category. Thencategoryneeds to be supplied here.
If you have uploaded data to tellusr using the file uploading endpoints, e.g. /tellusr/api/v1/{project}/upload-file,
then the recommended setting is to make semantic indexes use content_segment (and maybe a few other metadata fields).
This field is parsed from the pdfs/word-docs in such a way to that it represents semantically relevant chunks of the document with respect to the
document structure.
Do NOT select fields, such that their field-values combined becomes much longer than a hundred words.
So avoid using fields with large field values and instead rely on smaller fields like content_segment,
which is a chunked version of uploaded file content.
Only use fields whose content as text is descriptive of the document. Avoid numeric fields and attributes that
do not carry any semantically meaningful content.